What Are Coatings?
Coatings are a form of technology in which a film or surface treatment is applied to a substrate to achieve a function or feature.
Coatings are used in a wide variety of fields, including optics, electronics, automobiles, packaging, construction, and civil engineering.

Examples of Coatings
1. Reduce Glare from Plastic Film

Applying anti-glare (AG) coatings to plastic film gives glossy surfaces a matte finish. This improves visibility in outdoor and bright environments and reduces eye strain. They are mainly used for the screens of smartphones, computers, and other electronics.
2. Reduce Reflection from Plastic Film

Modern cars are increasingly incorporating larger navigation screens and digital instrument displays.
Applying anti-reflection (AR) coatings to screens and displays enhances visibility and safety.
3. Prevent Scratches and Stains on Plastic Film

Demand for electronic devices such as tablets has been increasing in recent years, especially in the education industry.
Applying a hard coating to the film on the screen of such devices helps prevent scratches and smudges caused by styluses.
4. Prevent Shards from Scattering upon Impact
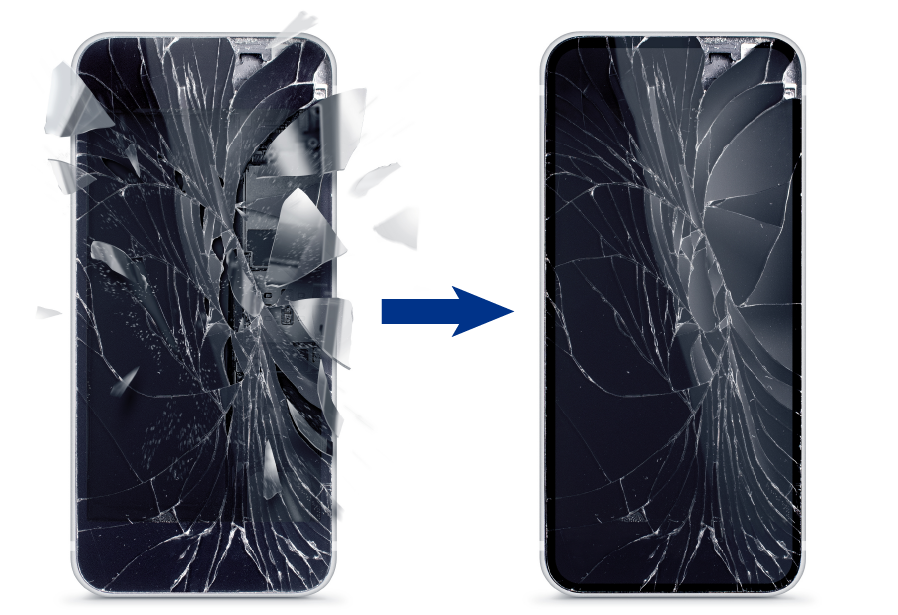

While electronic devices such as smartphones are becoming thinner and lighter, there is a growing demand to make these devices shatterproof as a safety measure if their screens break. Surface coating reduces the risk of glass shattering upon impact or when dropped.
5. Make It Easier to Wipe Off Fingerprints from Plastic Film
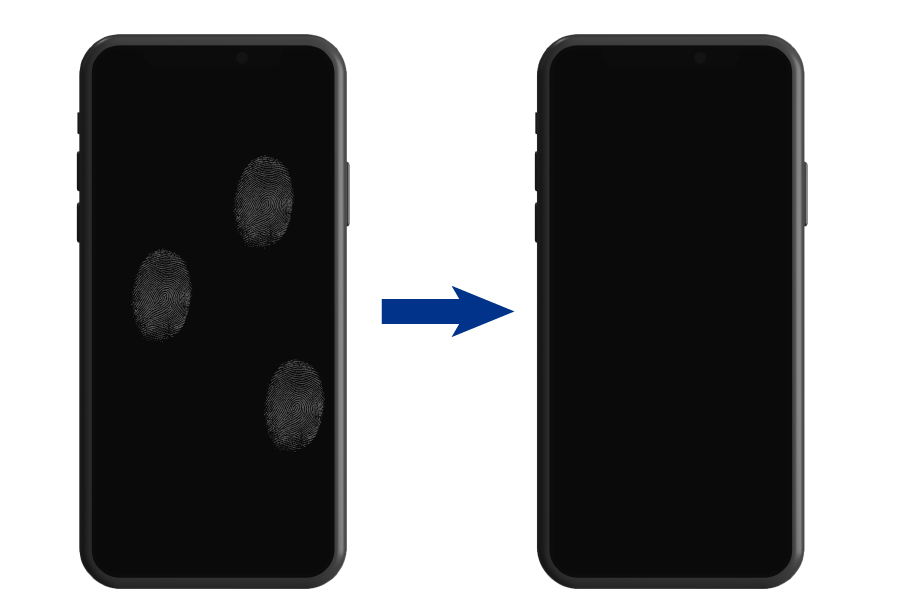
Anti-fingerprint (AF) surface treatment technology makes surfaces resistant to fingerprints and oily smudging, while also making it easier to wipe them off when they do appear. This helps maintain beautiful high-grade surfaces for a long time, including for smartphones, tablets, car interior components, and more.
Coating Process
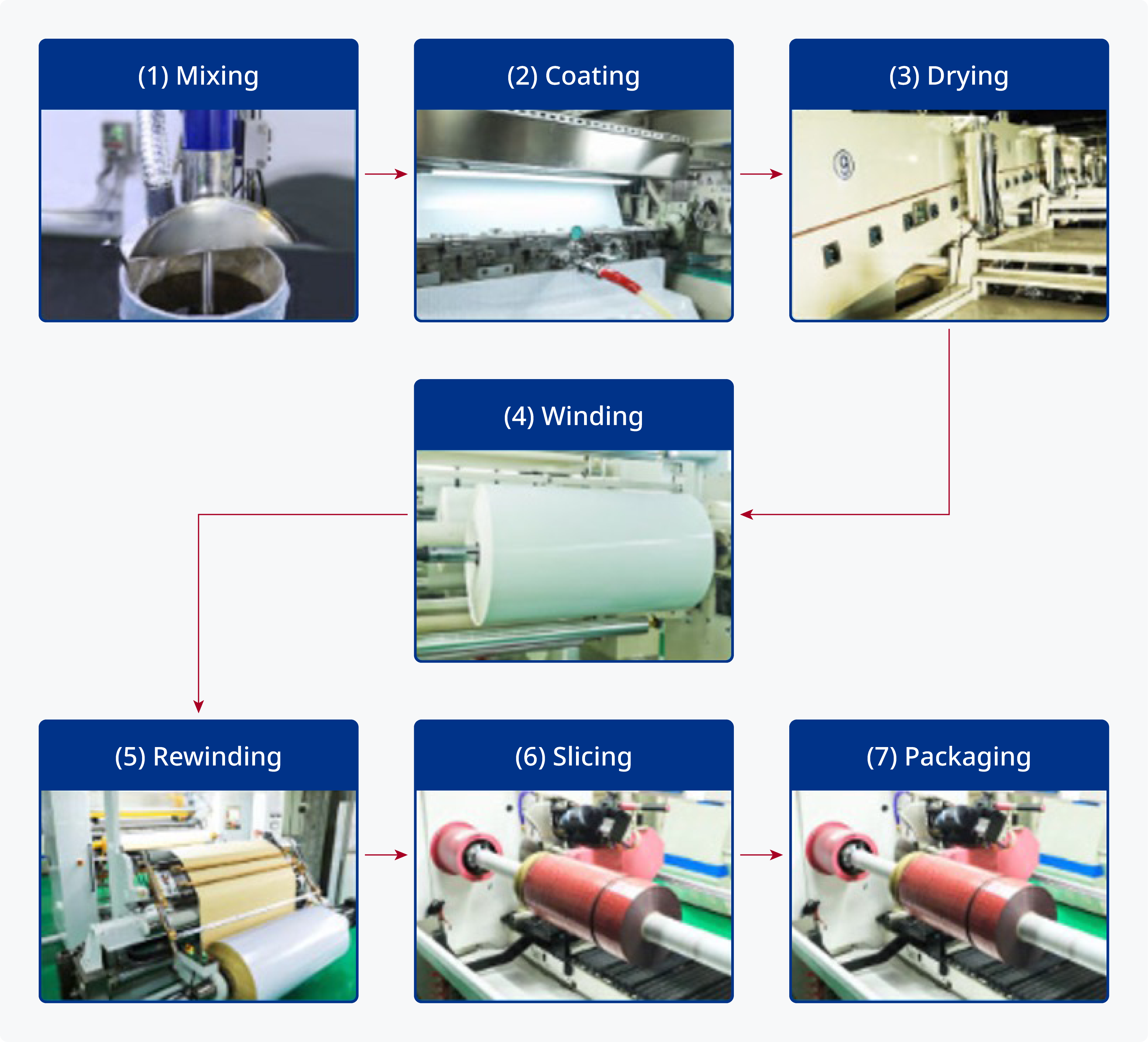
- 1. Mixing
Additives are added in the proper amount with the pressure-sensitive adhesive to be applied, and the coating liquid is mixed. - 2. Coating
The film thickness is set and the mixed coating liquid is applied to the substrate or release sheet.
Our services extend from general environmental coating to clean coating production lines. - 3. Drying
Under proper drying conditions, the coated liquid is poured off and the solvents in the coating are dispersed. - 4. Winding
The original roll of the dried tape is wound. - 5. Rewinding
The original roll is rewound according to the length of the tape to be sold. - 6. Slicing
The rewound product is sliced to provide tape up to 5 mm wide. - 7. Packaging
We perform everything from individual packaging to pallet packaging to specification.
Our services include the application of adhesive tapes and surface coatings—ranging from hard coats to anti-glare, anti-reflective, and anti-fingerprint finishes. One-stop processing is also available upon request, so please feel free to consult us.
